Technische Universität Berlin Picosatellite EXperiment 6
TUPEX-6
Technische Universität Berlin is currently researching a new means of attitude control for pico-satellites, which is called pico-satellite fluid-dynamic actuators (pFDAs). Incorporating a system of four pFDAs in a satellite makes it possible to precisely control the satellites attitude (the direction the satellite is looking at). To demonstrate the ability to change attitude using the novel actuators, the system will be tested in microgravity.
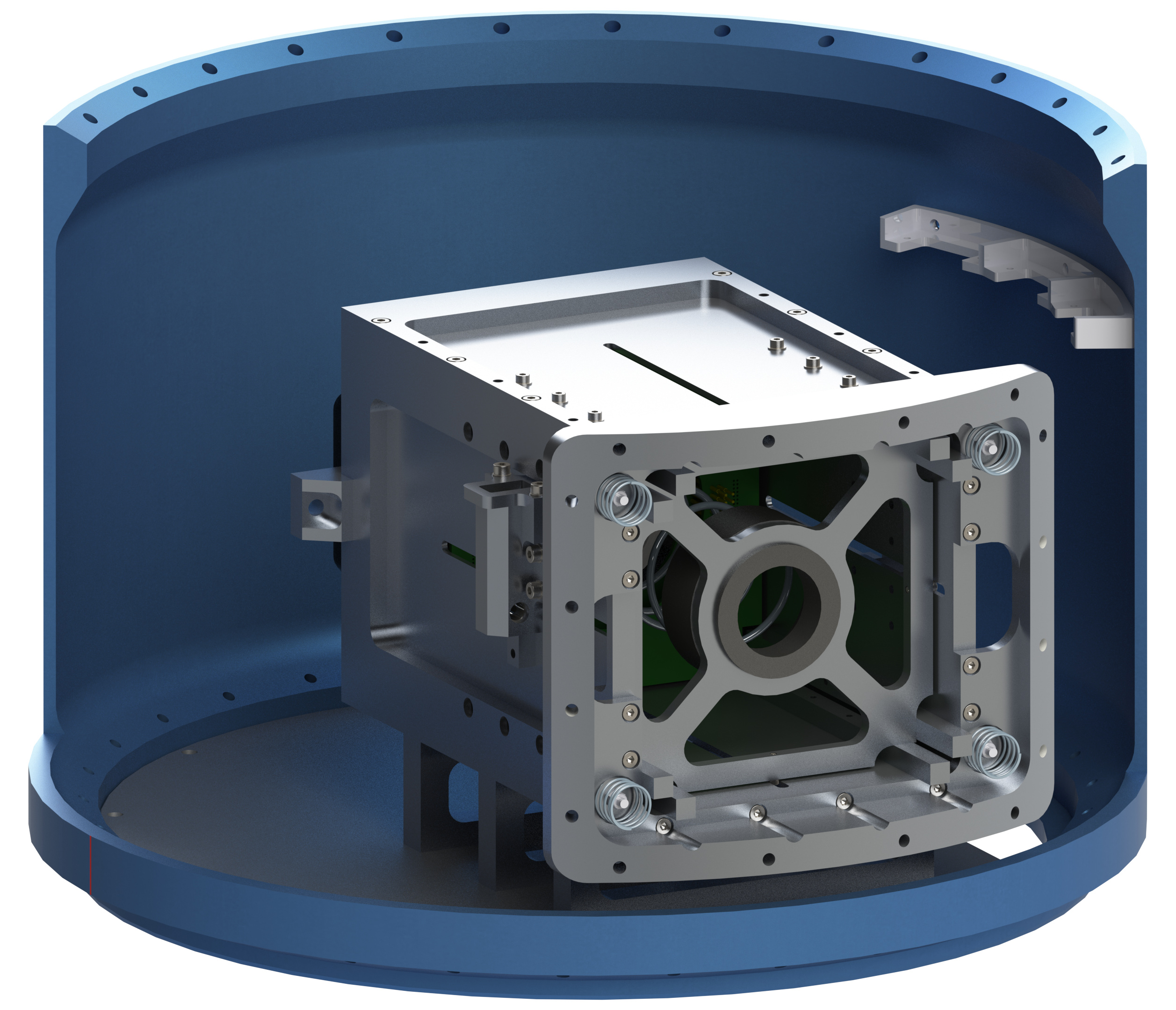
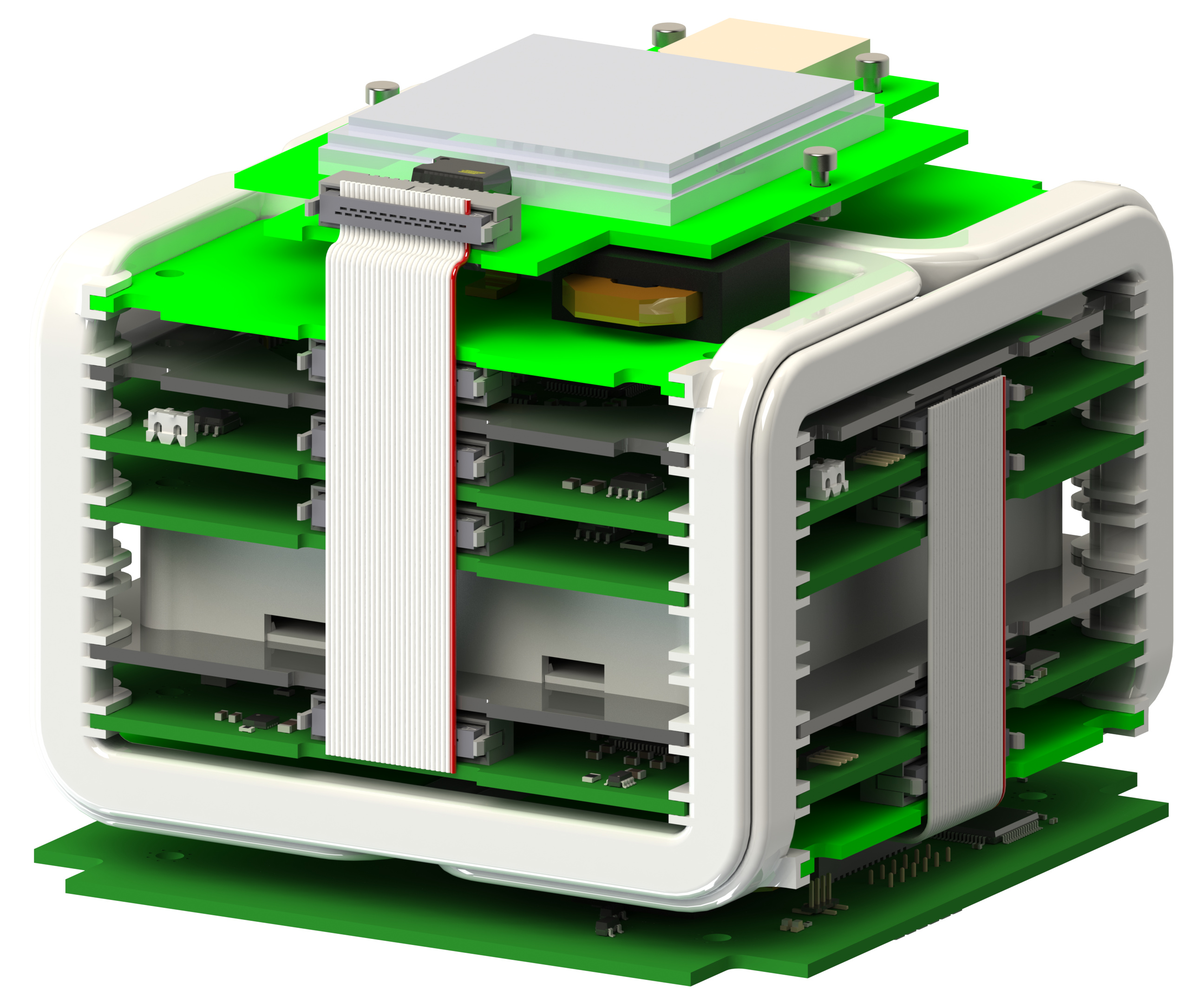
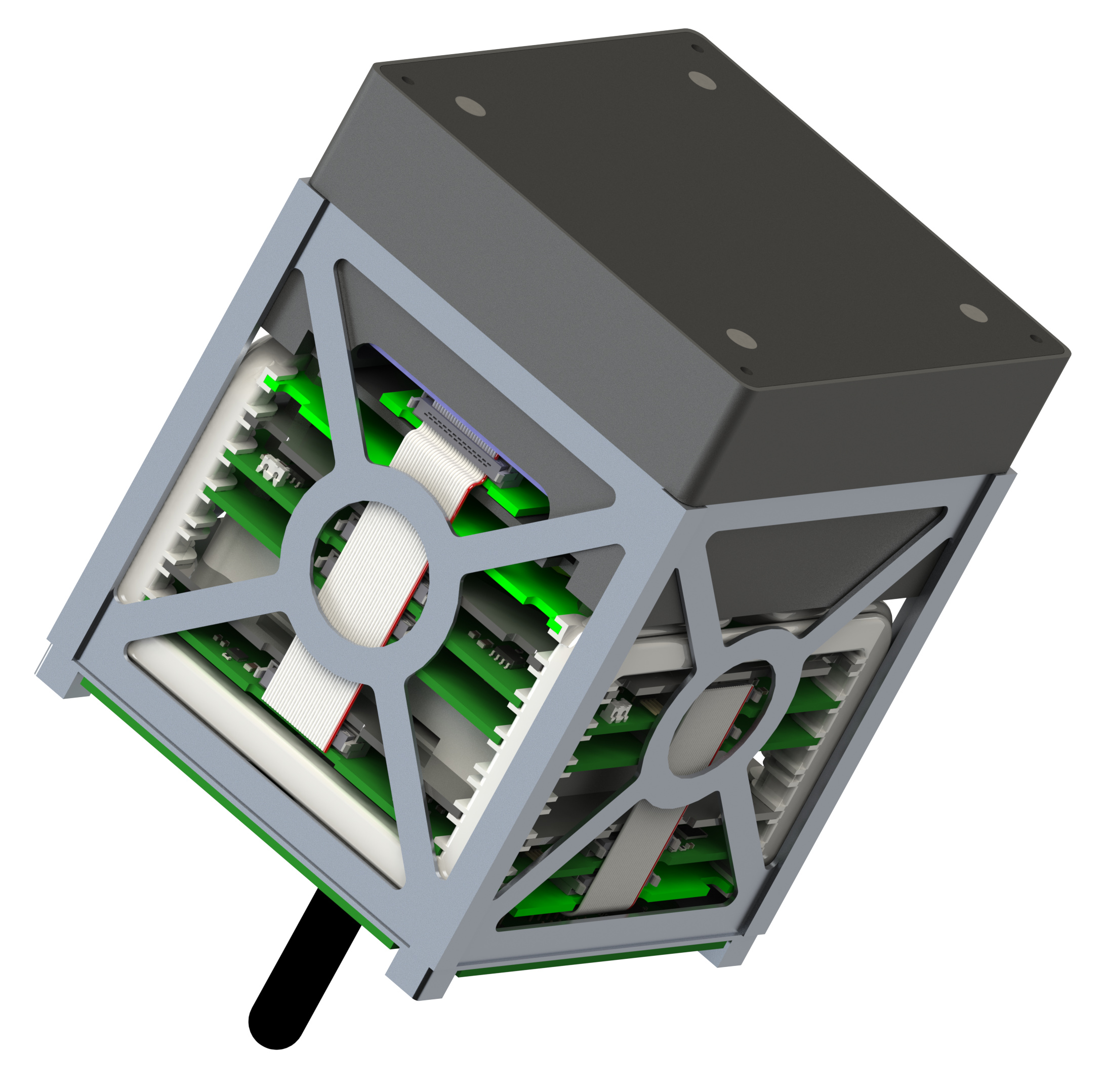
As participants in the REXUS/BEXUS-program, TUPEX-6 is provided with a launch onboard a REXUS rocket to experience up to two minutes of microgravity. The team is developing a free-falling unit (FFU) which hosts the pFDA attitude control system. The FFU resembles a single unit (1U) CubeSat and is being ejected from the rocket-borne equipment. The latter is being developed by the team, to be incorporated into the REXUS rocket.
The mission was initialized in September 2017. In November TUPEX-6 was selected as participant in the REXUS/BEXUS-program. For the Priliminary Design Review in February 2018, four team members were invited to the Esrange Space Center near Kiruna, Sweden. The following Cirtical Design Review in May 2018 was conducted at the German Aerospace Center (DLR) in Oberpfaffenhofen.
The upcoming Integration Progress Review will be conducted in August 2018 at Technische Universität Berlin. In December 2018 the last review will take place at the Center of Applied Space Technology and Microgravity (ZARM) in Bremen. All hardware required for the launch campign will be shipped from there to the launch site in Sweden. During the launch campaign in March 2019, the experiment will be integrated into the rocket and launched. Subsequent to the launch, gathered experiment data will be analyized. With completion of data analysis and the release of experiment result reports the mission is completed.
To learn more about the different parts of the mission, click the images.